Anatoxin-a (ATX) Detection Kit (Rapid – Recreational Water)
$268.75
In Stock & Ready to Ship
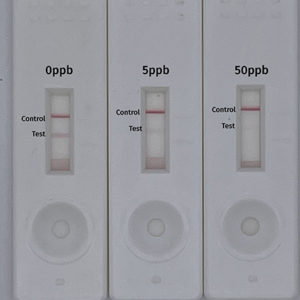
- Screening of Anatoxin in water samples at 7 ppb
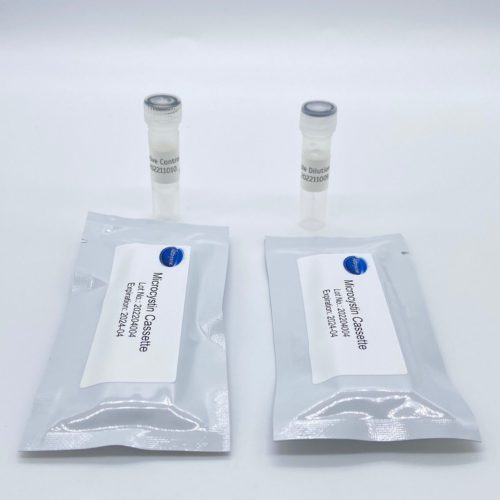
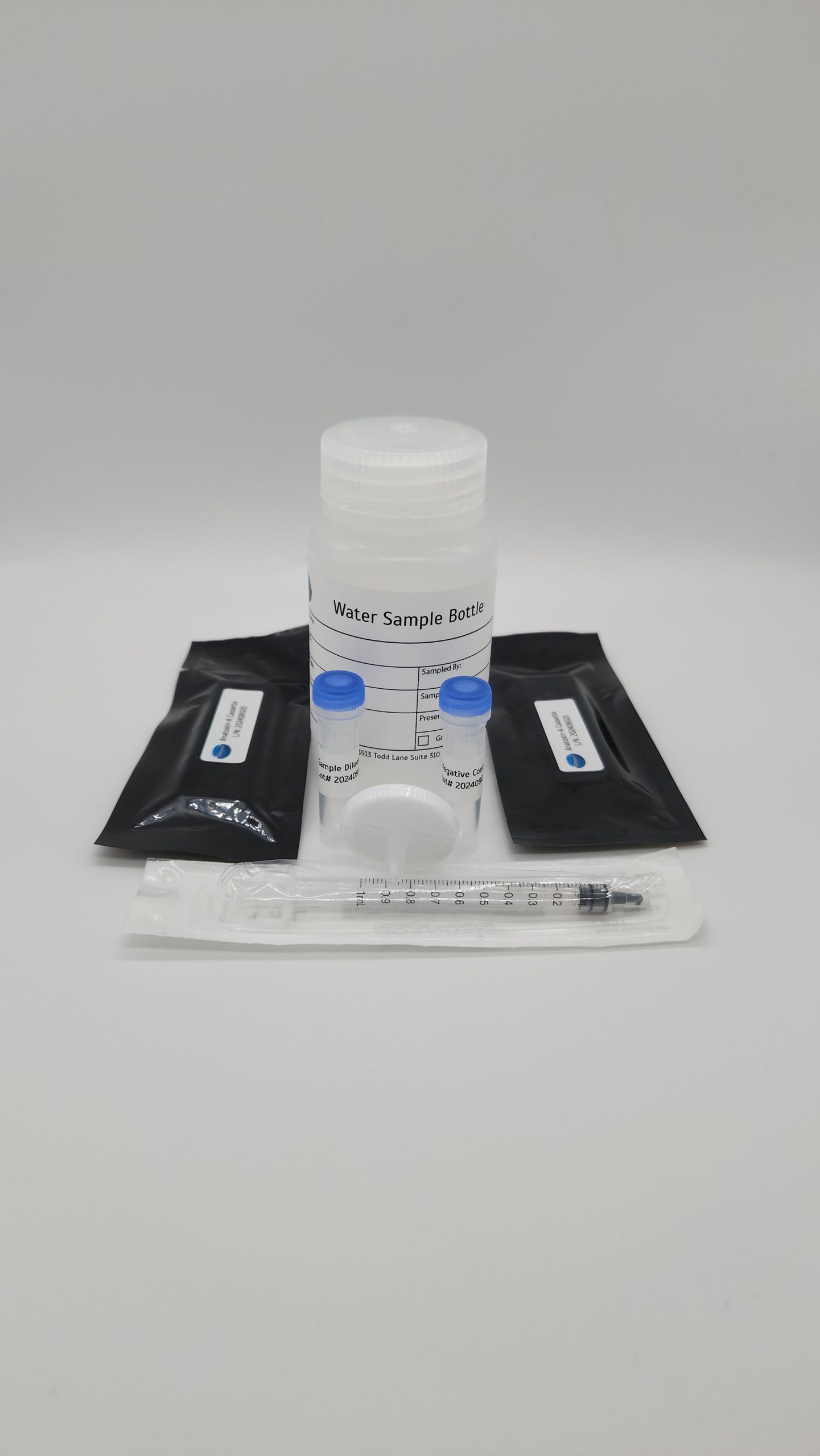
- Format: 10 tests (5 tests/5 control)
- Water Sample Bottles
- Negative Control
- 1mL Syringe
- Sample Dilution Buffer also sold separately
- Sample Filters
Attogene have developed patent pending technology which utilizes a stably assembled functional recombinantly expressed acetylcholine receptor (AChR) surrogate to the human alpha 4 beta 2 and alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor onto colloidal gold. The complex of AChR colloidal gold is embedded into a release matrix pad and dried. These AChR bound gold release matrix pads are applied to backing cards containing nitrocellulose sprayed with a specially designed nicotine conjugate (test line) and an independent control line. A wick and sample pad were applied to the backed cards, cut into strips and applied to cassettes. Our test responds to anatoxin-a in a concentration dependent and isomer specific fasion. On the other hand, the test line is not diminished by microcystin or other non-AChR ligands. Attogene has also demonstrated this test is able to detect AChR ligand toxins present in Oscillatoria brevis (UTEX B 1567), Anabaena flos-aquae (UTEX 2557), Anabaena subcylindrical (UTEX LB2382), UTEX 2497, UTEX 1611, UTEX 3013 Anabaena algae cultures. The test is stable, robust, rapid and easy to use analysis of ATX at or above 7 ppb. A lateral flow reader such as the RDS-2500 can be used to obtain numerical readouts of the line intensities making interpretation more reliable.
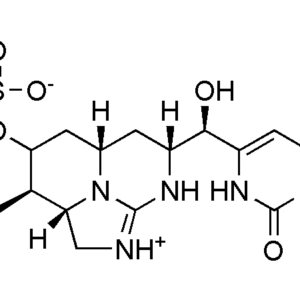
Anatoxin-a, also known as Very Fast Death Factor (VFDF), is a secondary, bicyclic amine alkaloid and cyanotoxin with acute neurotoxicity. It was first discovered in the early 1960s in Canada by P.R. Gorham in the early 1960s, after several herds of cattle died as a result of drinking water from Saskatchewan Lake in Ontario, Canada, which contained toxic algal blooms, and was isolated in 1972. The toxin is produced by multiple genera of cyanobacteria and has been reported in North America, South America, Central America, Europe, Africa, Asia, and Oceania. Symptoms of anatoxin-a toxicity include loss of coordination, muscular fasciculations, convulsions and death by respiratory paralysis. Its mode of action is through the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAchR) where it mimics the binding of the receptor’s natural ligand, acetylcholine. As such, anatoxin-a has been used for medicinal purposes to investigate diseases characterized by low acetylcholine levels. Due to its high toxicity and potential presence in drinking water, anatoxin-a poses a threat to animals, including humans.
State Anatoxin Thresholds for Recreation
- CA: Warning Value 20ppb, Danger Value: 90ppb
- CO: Caution Value 15ppb, Warning Value >15ppb
- IN: Advisory Value 8ppb, Prohibited Value 30ppb
- MN: Single Tier Recreational Value 7ppb
- MT: Tier 2 Caution Value 20ppb, Tier 3 Consider Closure Value >20ppb
- NJ: Advisory Value 15ppb
- OH: Single Tier Recreational Value 8ppb
- OR: Single Tier Recreational Value 15ppb
- PA: Recreation Advisory Value >8ppb, Avoid Primary Contact Value >300ppb
- TX: Tier III Danger Advisory Value: ≥60ppb
- UT: Warning Advisory Value >15ppb, Danger Advisory Value>90ppb
- VT: Single Tier Recreational Value 10ppb
- VA: Single Tier Recreational Value 8ppb
- WA: Danger Value >300ppb
- WV: Watch Value >80ppb, Warning Value 300ppb
- WY: Toxin Advisory Value 60ppb
- Confederated Tribes of the Coos, Lower Umpqua, and Siuslaw Indians: 15ppb
You may also like…
Microcystin Detection Kit (Rapid – Lab)
$129.00- Screening of Algae Toxins Microcystins and Nodularins
- Format: 10 tests (5 tests/5 control)
- Not provided: Water Sample Bottles
- Run Time: 10 Minutes
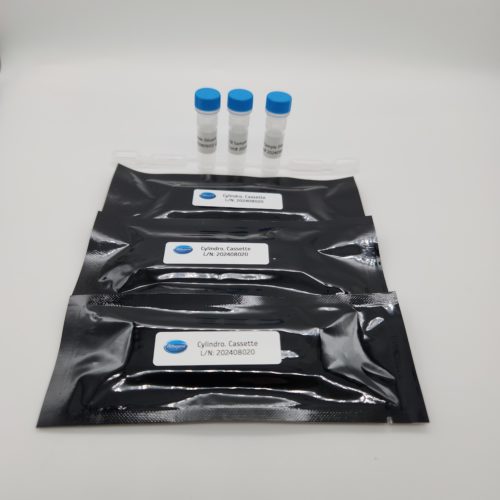
Cylindrospermopsin Detection Kit (Rapid – Freshwater Streams and Source Water)
$193.50
- Screening of Cylindrospermopsin in water samples at or above 30ppt
- Format: 15 tests (5 samples at 2 dilutions/5 controls)
- 5 – 10X Sample Dilution Buffer
- 5 – 1X Sample Dilution Buffer
- 5- Negative Control
- 10- Fixed Volume Pipettes
Microcystin Detection Kit (Rapid – Finished Drinking Water)
$155.88
- Screening of Microcystins in water samples at 0.1 ppb (drinking water)
- Format: 10 tests (5 tests/5 controls)
- Not provided: Water Sample Bottles
- Run Time: 15 Minutes
- Finished Drinking Water