High quality products to support Pathologists and Biological and Environmental Scientists
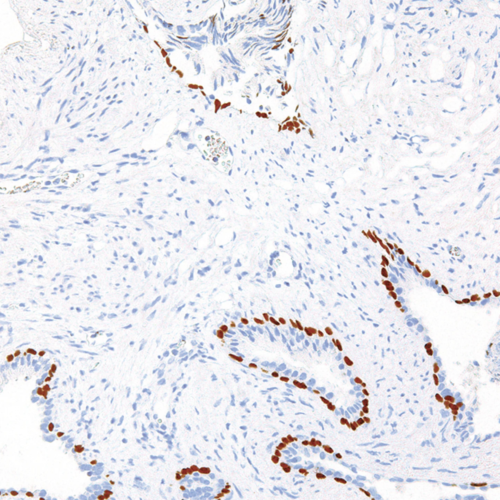
GeneAb™ hENT1
$182.75 – $843.88The Human Equilibrative Nucleoside Transporter 1 (hENT1) mediates the cellular uptake of physiologic nucleosides, including adenosine, as well as many anti-cancer drugs including gemcitabine, cytarabine, and decitabine. Deficiency of hENT1 can lead to resistance of such drugs, and the abundance of hENT1 protein in the plasma membrane is a major indicator of the efficiency and clinical outcome of these anti-cancer nucleosides.
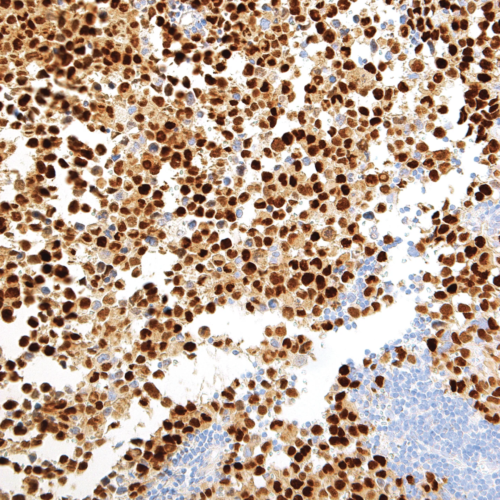
GeneAb™ p16 INK4A
$145.12 – $585.88The p16 (p16INK4A) protein is a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor that plays an important regulatory role in the cell cycle. By controlling the transition between the G1 and S phases through regulation of retinoblastoma protein, p16 decelerates cellular differentiation and therefore acts as a tumor suppressor, making it the key marker in several human cancers including head and neck cancer, perianal lesions, melanomas, gliomas, lymphomas, and some types of leukemia. p16 is also clinically indicated in carcinomas of the esophagus, pancreas, lung, biliary tract, liver, colon, and urinary bladder.
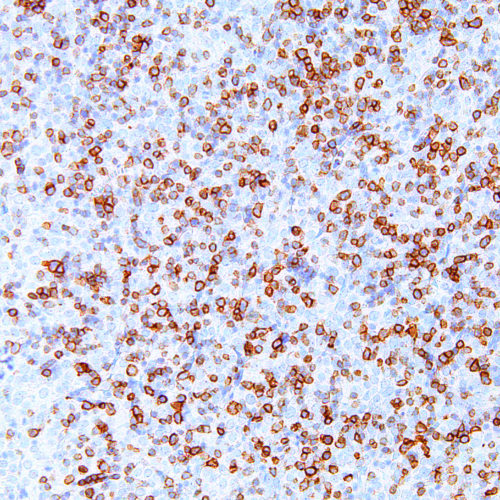
GeneAb™ CD45RA
$69.88 – $225.75CD45R, also known as MB1, is an isoform of CD45 that is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTPase) family. CD45R is expressed specifically on the surface of hematopoietic cells, and has demonstrated function as a regulator of the antigen and cytokine receptor signalling of B and T cells. Given that the antigen is located in the membrane of all B cells, with the exception of plasma cells and some mature T cells, Anti-CD45R exhibits specific reactivity with most B lymphocytes. The use of Anti-CD45R is primarily useful in distinguishing B cell lymphomas from T cell lymphomas, with specific reactivity to follicle center cells, mantle cells, some medullary thymocytes, and 80% of B cell lymphomas.
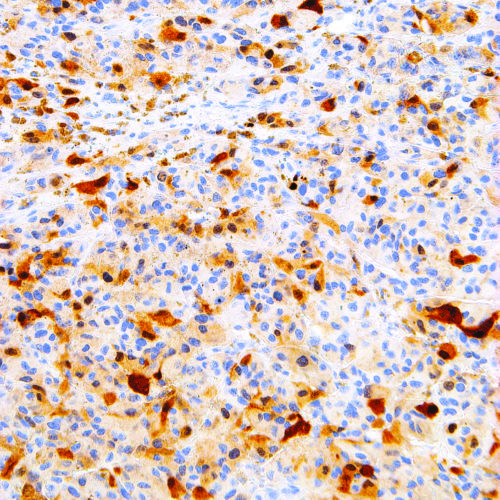
GeneAb™ S-100
$75.25 – $290.25S-100 is a low-molecular weight protein that is found in Schwann cells, melanocytes, glial cells, histiocytes, lipocytes, skeletal and cardiac muscle, chondrocytes, adipocytes, myoepithelial cells, macrophages, Langerhans cells, dendritic cells, and keratinocytes. S-100 is a useful marker for Schwann cell-derived tumors, as well as a number of well-differentiated tumors of the salivary gland, adipose and cartilaginous tissue. Anti-S-100 is used to detect melanomas, histiocytosis X, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors, and clear cell sarcomas.
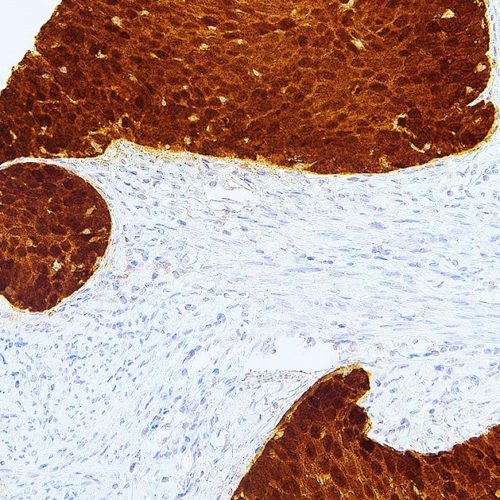
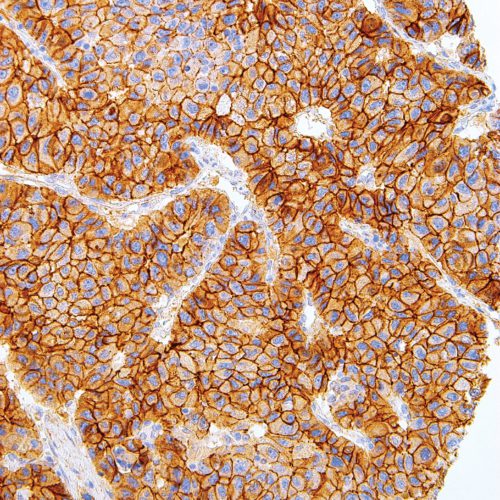
GeneAb™ p63
$182.75 – $913.75p63 is a tumor suppressor protein that is very similar to p53 in structure and function, while being homologous to p73. p63 is important in development and differentiation, and has been identified as a useful marker for distinguishing between lung squamous cell carcinomas and adenocarcinomas. Anti-p63 is also used to differentiate between benign and malignant prostate and breast lesions, due to its labeling of the nuclei of myoepithelial cells in both tissue types.
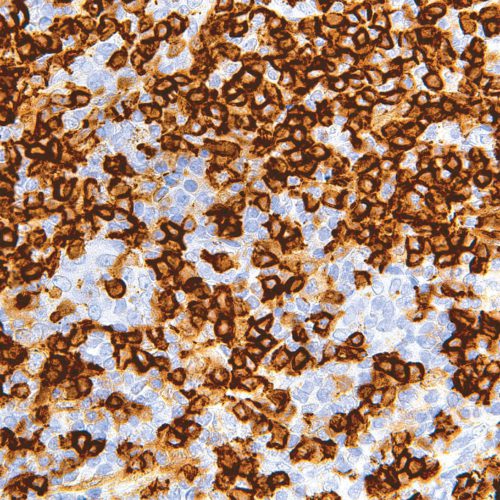
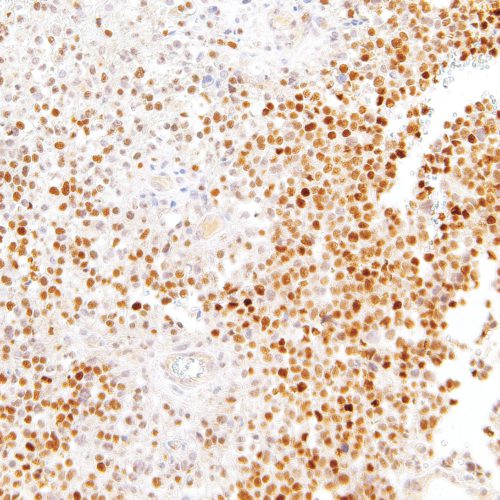
GeneAb™ SOX-11
$134.38 – $548.25SRY (Sex Determining Region Y)-Box 11 (SOX-11), also known as transcription factor SOX-11, is a nuclear transcription factor that acts in regulation of embryonic development and in cell differentiation. SOX-11 is expressed in the development of the human central nervous system, medulloblastoma, and glioma, and has been indicated as a marker for both Cyclin D1-positive and negative mantle cell lymphomas, Burkitt lymphoma, and lymphoblastic lymphoma.
GeneAb™ N-cadherin
$225.75 – $1,053.50N-cadherin, also known as Cadherin-2 (CDH2) or Neural Cadherin (NCAD), is a transmembrane cell adhesion molecule that was originally detected in nervous tissue. It plays an important role in embryogenesis, being involved in gastrulation and neural crest development. N-cadherin is found is cancer cells and allows for transendothelial migration, which is a critical process in the metastasis of cancer. Overexpression and disorderly arrangement of N-cadherin has been noted in dilated cardiomyopathy. It has been suggested that, when considered in adjunct with the status of a number of additional cell-cell adhesion molecules, missense mutations in N-cadherin may be a potential indicator of obsessive-compulsive disorder and Tourette disorder.
GeneAb™ Myogenin
$102.12 – $408.50Myogenin belongs to a family of myogenic transcription factors, including MyoD, myf5, and MRF4, which are critical in muscle development. Myogenin is found strictly in cells of skeletal muscle origin, and is therefore used as a biomarker for tumors of the muscle lineage, including alveolar rhabdomyosarcomas. Anti-Myogenin staining may occur in Wilms’ tumor, and labels the nuclei of myoblasts in developing muscle tissue. It is also expressed in some leiomyosarcomas.